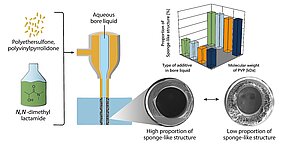
Researchers of the research department Surfaces of Porous Membrane Filters at the IOM have investigated an alternative to conventional, environmentally harmful solvents for membrane production: N,N-dimethyl lactamide (Agnique® AMD 3L), a solvent that is more environmentally friendly and can be used to produce PES hollow fiber membranes. The core findings are as follows: Using a Design of Experiments (DoE) approach, the team successfully identified the optimal conditions to produce macrovoid-free, sponge-like membrane structures, which are known for their superior mechanical strength and uniform pore distribution. Crucially, the team found that high-molecular-weight PVP (360 kDa) was essential for forming stable sponge-like morphologies.
In summary: Environmentally friendly solvents like N,N-dimethyl lactamide has the potential to yield two key benefits: the production of high-performance membranes and the reduction of the lower ecological footprint. This dual benefit is a significant advancement in the field of sustainable separation technologies, offering a mutually beneficial solution to both environmental and economic concerns.
This study establishes a solid foundation for future solvent replacement strategies and greener membrane manufacturing processes.
The results were recently published:
Konrad H. Leopold, Daniel Breite, Martin Schmidt, Andrea Prager, Marco Went, Mathias Kühnert, Dirk Enke, Agnes Schulze
Design of sponge-like PES hollow fiber membranes using the environmentally friendly solvent N,N-dimethyl lactamide
Separation and Purification Technology, Vol. 365, 132625 (2025)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.132625