Atmospheric plasma jet machining (PJM) is a technique for precision freeform optics manufacturing. PJM of fused silica is established at IOM for several years and is part of the Ion beam and plasma jet based ultra-precision surface figuring topic of the Ultra-precision Surfaces research area. Continuous development of the process targets at its applicability to a larger variety of optical glasses.
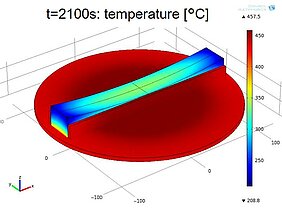
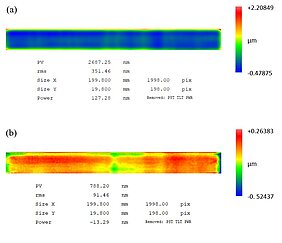
Intensive basic research has been undertaken to elucidate the plasma-surface interaction mechanisms during borosilicate glass etching. The recent paper presents an optimization of the PJM process resulting in the ability to perform figure error corrections of an optical element made of borosilicate crown glass. In order to cope with the workpiece dimensions, dynamic surface temperature variations and thus varying etch rates that influence the dwell-time based material removal, a simulative approach was chosen and the model was validated by experiments. Finally, it could be shown that with the optimized process the figure error of an optical element could be reduced by up to 74%.
The results of the research have now been published in the Journal of the European Optical Society:
Atmospheric Plasma Jet processing for figure error correction of an optical element made from S-BSL7
H. Müller, T. Waak, U. Birnbaum, G. Böhm, T. Arnold; J. Eur. Opt. Society-Rapid Publ. 2022, 18, 4
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/jeos/2022003