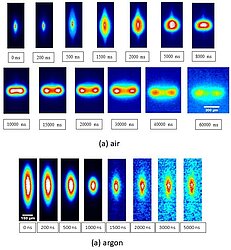
Plasma produced by tight focusing of a femtosecond laser in gases has surprisingly dissimilar dynamics in air and argon. Researchers from the groups Laser based micro- and nanostructuring and Plasma-assisted deposition of thin films at IOM Leipzig have determined that this is due to the differences in electron temperatures of the plasma produced in these gases. They determined the 2D distribution of electron temperature by means of optical emission spectroscopy and used the 2D profile as an initial condition for fluid dynamic simulations. Simulations show that the plasma dynamics, which is driven by baroclinic torque, induces stronger vortices in air than in argon.
More information in the publication:
Dynamics and 2D temperature distribution of plasma obtained by femtosecond laser-induced breakdown
Afaque M. Hossain, Martin Ehrhardt, Martin Rudolph, Dmitry Kalanov, Pierre Lorenz, Klaus Zimmer, André Anders
Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 55 (2022) 12, 125204
https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac42f8